Human IL-1α & IL-1β Reporter HEK 293 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
HEK-Blue™ IL-1β Cells HEK 293 reporter cells for human and murine IL-1β cytokines |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-il1bv2
|
|
||
|
HEK-Blue™ IL-1β vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-il1bv2-av
|
Notification: Reference #hkb-il1bv2-av can only be ordered together with reference #hkb-il1bv2.
Human IL-1 Reporter Cells

Signaling pathway in HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells
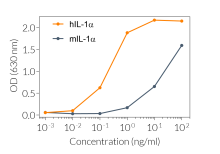
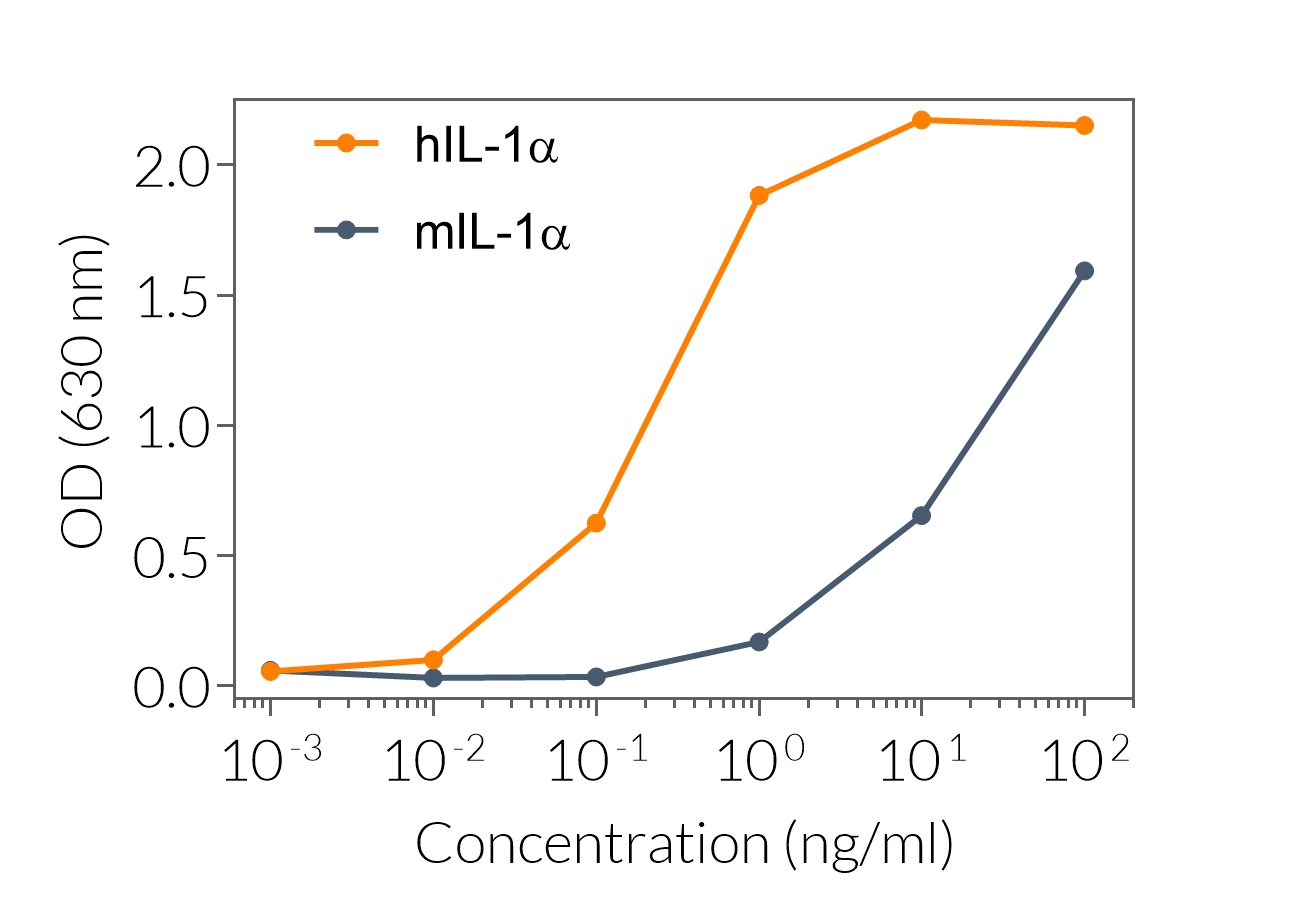
HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells were engineered from the human embryonic kidney HEK293 cell line to detect bioactive human interleukin-1 β (IL-1β) in various biological samples (cell culture supernatant and serum) by monitoring the activation of the NF-κB and AP-1 pathways. These cells are useful to monitor IL-1β secretion in inflammasome activation studies. Additionally, HEK-Blue™ IL-1β detect bioactive human IL-1α. Both IL‑1α and IL-1β are secreted pro‑inflammatory cytokine that play a critical role in immune responses and inflammation [1].
Cell line description:
HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells endogenously express the human (h) IL-1 receptor, which binds both IL-1α and IL-1β. They were transfected with a NF-κB/AP-1-inducible secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter. The binding of IL-1α or IL-1β to its receptor triggers a signaling cascade leading to NF-κB/AP-1 activation and the subsequent production of SEAP. This can be readily assessed in the supernatant using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent.
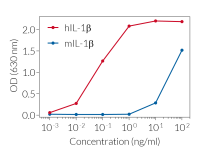
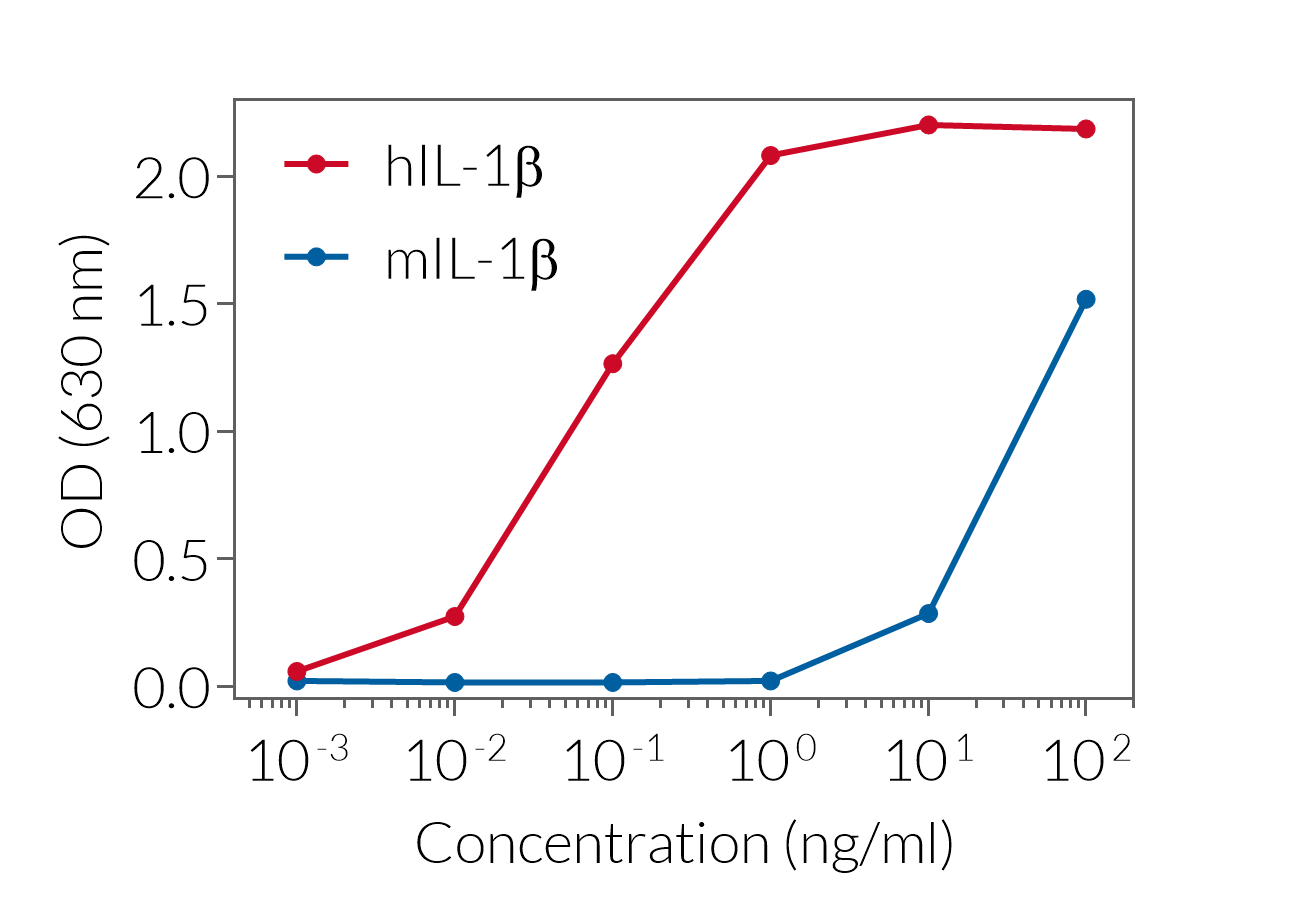
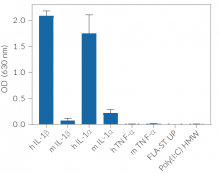
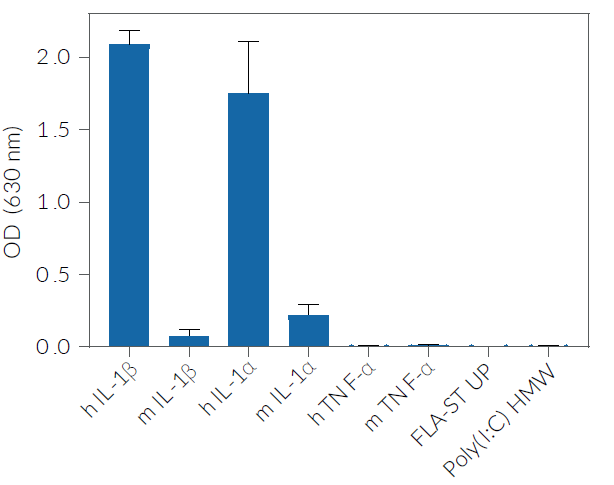
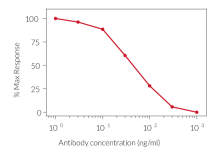
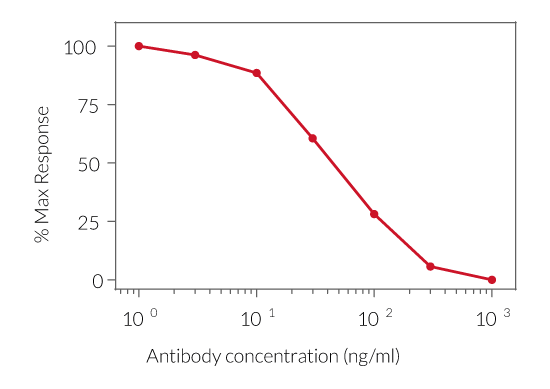
HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells respond to hIL-1α and hIL-1β (see figures). They also respond to a lesser extent to murine (m) IL-1α and mIL-1β (see figures). The specificity of the HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells for the detection of IL-1α or IL-1β can be confirmed using a neutralizing antibody against human IL-1α or IL-1β, such as anti-hIL-1α-IgG and anti-hIL-1β-IgG. Of note, these cells do no respond to hTNF-α or mTNF-α (see figures).
Key features:
- Fully functional IL-1β signaling pathway
- Readily assessable NF-κB/AP-1-inducible SEAP reporter activity
- Do not respond to human or murine TNF-α
Applications:
- Detection of human IL-1β, and to a lesser extent murine IL-1β
- Detection of IL-1β in inflammasome studies
- Screening of anti-IL-1β antibodies
HEK-Blue™ IL-1β and HEK-Blue™ IL-1R cells
- HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells are more sensitive to human IL-1 isoforms than murine isoforms. We recommend using this cell line to test supernatant from human inflammasome cellular assays.
- HEK-Blue™ IL-1R cells are stably transfected to additionally express the murine IL-1R, conferring a higher sensitivity to mIL-1α and mIL-1β, when compared to HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells.
![]() Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes
Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes
Reference:
1. Dinarello C., 2018. Overview of the IL-1 family in innate inflammation and acquired immunity. Immunol Rev. 281(1): 8–27.
Back to the topSpecifications
Antibiotic resistance: Zeocin®
Growth medium: DMEM, 4.5 g/l glucose, 2 mM L-Glutamine, 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 µg/ml Normocin™
Guaranteed mycoplasma-free
Detects human and murine IL-1β (α)
- Detection range for human IL-1β: 100 pg - 100 ng/ml
- Detection range for murine IL-1β: 10 ng - 1 µg/ml
This product is covered by a Limited Use License (See Terms and Conditions).
Back to the topContents
- 1 vial containing 3-5 x 106 cells
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
IL-1β is a soluble pro-inflammatory cytokine that plays a critical role in the host response to infection and injury [1]. It is synthesized as a pro-IL-1β zymogen by activated macrophages and must be cleaved by caspase-1 to generate its mature form [2]. IL-1β binding to the IL-1R1 receptor triggers the formation of the IL-1R1/IL-1R3/MyD88 complex and induces signaling leading to the activation of the transcription factors NK-κB and AP-1 [3]. Due to its role in mediating acute and chronic inflammation, IL-1β has emerged as a therapeutic target for auto-inflammatory diseases [1,4].
1. Dinarello C., 2018. Overview of the IL-1 family in innate inflammation and acquired immunity. Immunol Rev. 281(1): 8–27.
2. Lopez-Castejon G. & Brough D., 2011. Understanding the mechanism of IL-1β secretion. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22(4):189-95.
3. Weber A. et al., 2010. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) pathway. Sci Signal. 3(105):cm1.
4. Dinarello CA., 2011. Interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Blood. 117:3720–3732.
THP-1/HEK-Blue™ IL-1β Assay

1. Production of IL-1β by THP-1 cells. Typically, THP-1 cells are pre-treated with phorbol 12-myristate acetate (PMA) to become more susceptible to inflammasome activators, then are primed with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). These treatments induce the production of pro-IL-1β, the immature form of IL-1β. Subsequent stimulation with inflammasome inducers, such as ATP, leads to NRLP3 and caspase-1 activation resulting in IL-1β maturation and secretion.

2. Detection of IL-1β by HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells. IL-1β-containing THP-1 supernatants are added to HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells leading to NF-κB activation and the subsequent production of SEAP. The presence of SEAP in HEK-Blue™ IL-1β supernatants is assessed using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection medium.
Back to the top